European Commission announces Galileo’s first services
The first services provided by the European navigation system Galileo are available as of today, the European Commission announced yesterday. The latest simultaneous launch of four Galileo satellites on 17 November brings the total number of currently active satellites to 18. The Galileo Reference Centre is currently being built in Noordwijk, the Netherlands. Starting next year, this centre will have an important role in preserving the quality of the provision of Galileo’s services.
What is Galileo and what is its added value for society and the economy?
Q&A to answer the questions on What, When, How and Who:
What?
What is Galileo?
 Galileo is the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) of the European Union. It is comparable to GPS of the United States and delivers radio signals for the purpose of positioning, navigation and timing. Once it is fully operational, Galileo will provide five services: the open service, the public regulated service, the commercial service and the search and rescue service, as well as contributing to the integrity monitoring service.
Galileo is the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) of the European Union. It is comparable to GPS of the United States and delivers radio signals for the purpose of positioning, navigation and timing. Once it is fully operational, Galileo will provide five services: the open service, the public regulated service, the commercial service and the search and rescue service, as well as contributing to the integrity monitoring service.
What are Galileo’s initial services?
Galileo is currently being rolled out; in other words, the satellite and ground station infrastructure are being extended. The provision of the initial services heralds a new phase for the system: from roll-out and test phase to an operational system. The commissioning of the initial services means that all devices on the market intended for the general public, such as smartphones and vehicle navigation devices, will be able to use the signals from Galileo for positioning, navigation and timing if they are equipped with a Galileo-compatible chipset.
Galileo’s initial services are the first step towards its being fully operational. The Galileo system will be expanded further with additional satellites to extend the constellation, which will gradually improve the system’s worldwide performance and availability. The constellation is expected to be completed in 2020.
The initial services offered by Galileo are the Open Service, the Public Regulated Service (PRS) and the Search and Rescue Service (SAR).
What is Galileo’s open service?
Galileo’s open service is a free service for positioning, navigation and timing intended for the general public. The service can be used by various devices, such as smartphones and car navigation systems, which are equipped with Galileo-compatible chipsets.
What is Galileo’s public regulated service?
The public regulated service is intended for users authorised by government such as civil protection, the fire service, customs officers and the police. The service is extremely robust and fully encrypted, so that in the event of emergency or crisis situations, such as terrorist attacks, the continuity of the service provision for government-authorised users is guaranteed.
What is Galileo’s search and rescue service?
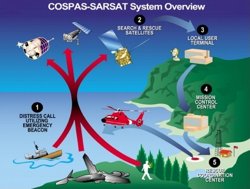 Galileo’s search and rescue service is the European contribution to ‘Cospas-Sarsat’, the international system for the localisation of distress beacons, which it will substantially improve. The time needed to find someone in distress at sea or in the mountains who activates a distress beacon will be reduced from its current maximum of three hours to only ten minutes. The position of the beacon will also be more accurately pinpointed to within a range of 5 km: an improvement compared to the current 10 km.
Galileo’s search and rescue service is the European contribution to ‘Cospas-Sarsat’, the international system for the localisation of distress beacons, which it will substantially improve. The time needed to find someone in distress at sea or in the mountains who activates a distress beacon will be reduced from its current maximum of three hours to only ten minutes. The position of the beacon will also be more accurately pinpointed to within a range of 5 km: an improvement compared to the current 10 km.
What is the Galileo Declaration of Initial Services?
The European Union’s Declaration of Galileo’s initial services is to publicise the fact that Galileo’s satellites and ground station infrastructure are ready for use. The conditions under which Galileo’s initial services will be provided, such as expected performance (accuracy, etc.) and availability are available on the website of the European GNSS service centre: www.gsc-europa.eu.
What are the advantages of Galileo’s initial services for end users?
Galileo’s initial services will be fully interoperable with GPS and their combined use will have many benefits for the end user. More satellites will be available due to the combination of Galileo satellites and GPS. The significance for end users is that positioning will be more accurate and more reliable. This increased accuracy in terms of positioning will especially improve navigation in cities where tall buildings often obstruct satellite signals.
Furthermore, due in part to Galileo’s accurate timing, the synchronisation of financial and bank transactions and of telecommunication and energy distribution networks will benefit in terms of resilience, which will help to improve their efficiency. Although this is not very visible, it is essential.
Finally, Galileo will help save lives. Galileo’s search and rescue service reduces the time needed to detect distress beacons from the current maximum of three hours to only ten minutes. Given that the beacons will also be localised more accurately, the rescue of people in distress at sea or in the mountains will be speeded up.
Which Galileo-compatible devices are available on the market?
The market is ready for Galileo. There were only three manufacturers producing devices with Galileo-compatible chips in 2010. There are now 17 companies producing such chips, representing more than 95% of the worldwide supply.
These include:
- important manufacturers of chipsets such as Broadcom, Mediatek, STM, Intel, Qualcomm and uBlox;
- Qualcomm, the market leader for chips for smartphones such as Snapdragon. Qualcomm is already making all its devices compatible with Galileo; many smartphones are therefore ready to use Galileo.
- STM, a leading European manufacturer of chipsets in the automobile sector. STM has announced Galileo-compatible ‘Teseo’ chips for telematics in vehicles and navigation systems.
The Spanish manufacturer of mobile phones, BQ, introduced the first Galileo smartphone to be developed in Europe onto the market in September 2016.
Furthermore, Galileo will be available in every new vehicle with type approval to be sold in Europe from 2018; that means that the emergency response system eCall will also be available for use.
The continuously growing list of devices and chipsets that are already available and compatible with Galileo can be found on www.useGalileo.eu.
What are the socioeconomic consequences of Galileo?
The benefits of Galileo can be measured by means of its socioeconomic effect on users, society and the environment.
Users will benefit from more reliable and more accurate positioning, which will particularly improve navigation in cities and built-up areas. Elements such as Galileo’s search and rescue service and its integration into the eCall system will shorten response times of emergency services in crisis situations or when accidents happen.
Additionally, the synchronisation of financial and bank transactions and of transactions relating to telecommunication and energy distribution networks that keep the world communicating will benefit in terms of resilience, thanks in part to Galileo’s accurate timing.
The use of satellite navigation has provided an impetus to global economic growth, especially in high-tech industries. Experts predict that the global market for satellite navigation will grow by more than 8% by 2019. The additional resilience that Galileo – as the third global system after GPS and GLONASS – will provide is expected to enable a whole range of new applications and services that will make use of its greater reliability in terms of positioning. This will stimulate economic growth in Europe and beyond even further.
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) has conducted additional research, which reveals that the use of Galileo and GNSS will generate considerable economic and ecological benefits in the coming decade; the research can be consulted on the website of the GSA www.gsa.europa.eu.
What sort of performance can I expect from Galileo?
Measurements of Galileo’s advanced navigation signals reveal that they perform extremely well. The accuracy that can be achieved depends on a number of factors, such as the number of satellites and system optimisation. The initial services are expected to perform as well as GPS and will improve further as the system reaches completion in 2020. More detailed data on performance (accuracy, etc.) and availability can be found on the website of the European GNSS service centre: www.gsc-europa.eu.
 The other freely available Galileo signals, which use different frequencies, will offer professional and more demanding users with specific receivers even better performance.
The other freely available Galileo signals, which use different frequencies, will offer professional and more demanding users with specific receivers even better performance.
When?
When will Galileo’s initial services be announced?
Galileo’s initial services will be announced soon.
When are Galileo’s services expected to be available?
All Galileo’s services will be available as soon as the constellation of the satellites and the ground station infrastructure have been completed, which is expected to be in 2020. Galileo will then be able to perform optimally and with maximum availability.
When will I be able to use Galileo on a mobile phone?
If you cannot do so already, then very soon! Leading manufacturers of chipsets for smartphones, including Qualcomm, Broadcom, Intel and Mediatek, are already selling products compatible with Galileo. The first Galileo-compatible phones came onto the market in autumn 2016 and many more will follow. It is very likely that all future smartphones and satellite navigation devices will be able to use Galileo and other global navigation satellite systems.
When will I be able to use Galileo in my car?
All new vehicles with type approval that are sold in Europe will be Galileo-compatible from 2018 as part of the obligation to comply with the regulation concerning the emergency response system eCall. Galileo-compatible satellite navigation devices for your car will be on the market from 2017.
Where?
Where can businesses find information to help them develop products and services that can use Galileo signals?
The European GNSS service centre is the point of contact for everything related to the development of products and services compatible with Galileo. The service centre can be contacted via: www.gsc-europa.eu.
How?
How will I know whether my phone or navigation system is compatible with Galileo?
The chipsets and smartphones that are currently compatible with Galileo can be found on www.useGalileo.eu. This tool will be updated as the list becomes longer!
How much will I have to pay for the initial services from Galileo?
The initial services from Galileo are free of charge and will remain so, even once the system is fully operational.
Who?
Who provides Galileo’s initial services?
The European Commission bears final responsibility for the Galileo programme but the European GNSS Agency (GSA) will provide the initial services.
The European Space Agency (ESA) is responsible for rolling out the system and for providing technical support for operational tasks on behalf of the European Commission.
Who can I contact for additional information about Galileo’s initial services?
The European GNSS service centre is there to assist all users of Galileo. The helpdesk at the service centre can be contacted via http://www.gsc-europa.eu.